Background of Israel-Lebanon Wars
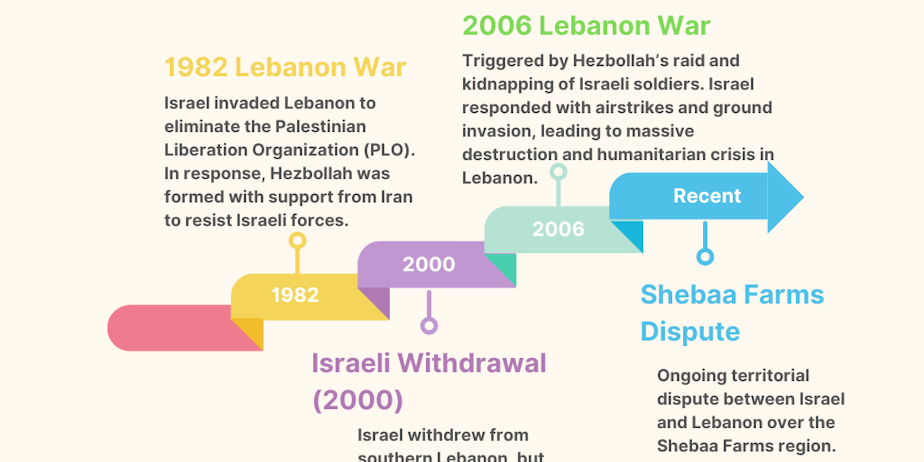
- Historical Conflicts: The Israel-Lebanon conflict has seen multiple wars and clashes, with the 1982 Lebanon War and the 2006 Lebanon War being the most significant.
Role of Hezbollah:
- Hezbollah, a Shiite militant group backed by Iran, has played a central role in this conflict. Formed in the 1980s, Hezbollah emerged as a reaction to Israel’s invasion of Lebanon in 1982.
- Hezbollah has since evolved into a key political and military force in Lebanon, frequently clashing with Israeli forces.
Israeli Invasions: Israel’s invasions in southern Lebanon were initially aimed at dismantling the Palestinian Liberation Organization (PLO), and later, Hezbollah became the target of Israeli operations.
Key Issues:
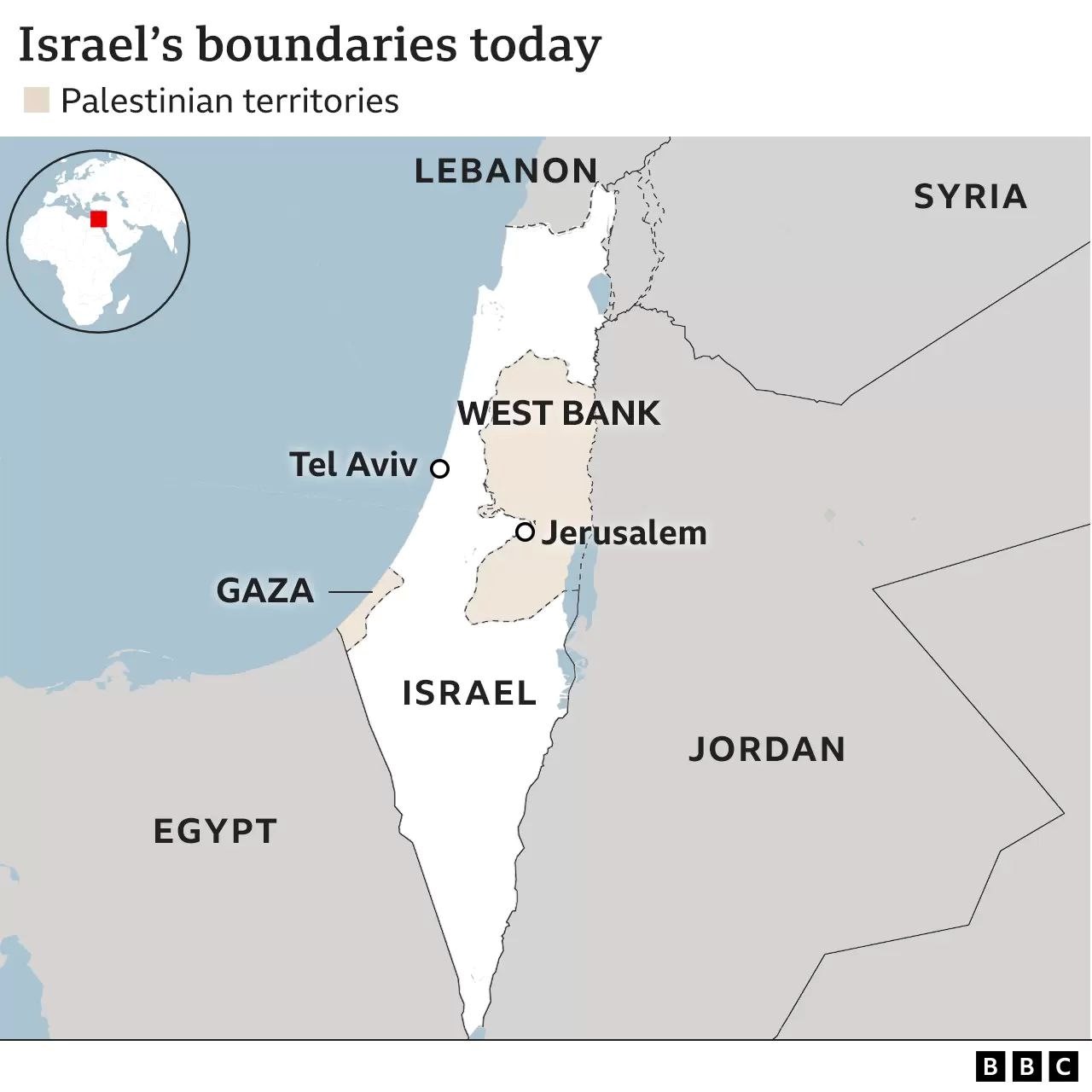
- Shebaa Farms Dispute: A territorial conflict between Lebanon and Israel over the Shebaa Farms, an area near the intersection of Lebanon, Israel, and Syria.
- Iran-Israel Proxy War: Iran’s financial and military support for Hezbollah fuels this conflict, with Hezbollah acting as an extension of Iranian influence in the region.
Global Impacts of the Israel-Lebanon War
- Geopolitical Realignment in the Middle East: The ongoing war disrupts the peace process and normalization efforts in the region, such as the Israel-Arab reconciliation and the Iran-Saudi détente.
- Middle East as a Theatre of War: The Middle East has historically been a conflict zone, with wars like the Gulf War and Iraq War. The involvement of foreign powers like the S. and EU in the Israel-Lebanon war may escalate tensions further, making it a site for proxy wars.
- Disruption of Global Connectivity Projects: Projects like the India-Middle East Economic Corridor (IMEC) are at risk. The conflict endangers strategic supply routes, such as the Strait of Hormuz and the Red Sea, crucial for global trade.
- Global Supply Chain Disruptions and Inflation: The conflict threatens oil production and supply chains, further exacerbating global inflation, which has already been affecting economies worldwide.
- Radicalization: The war could serve as a rallying point for extremist groups like al-Qaeda or ISIS, framing the conflict as a jihad against Israel and the West, potentially increasing recruitment and regional instability.
Impact of the Israel-Lebanon Conflict on India
- Impact on India’s De-hyphenation Policy: India has successfully balanced relations with both Israel and the Arab World. However, this conflict puts India in a diplomatic dilemma, potentially complicating its strategy in West Asia.
- Inflation and Oil Prices: The war affects oil and gas production, leading to increased oil prices. India, being heavily reliant on imported oil, could face further inflationary pressures.
- Depreciation of the Indian Rupee: Higher oil prices and uncertainty in the global financial markets may lead to an increase in India’s Current Account Deficit (CAD) and a depreciation of the rupee.
- Impact on India-Israel Trade: Israel is a key defence and strategic partner for India. Involvement in a prolonged conflict could reduce trade and cooperation between the two countries, affecting sectors like defence and technology.
- Diaspora and Remittances: India’s large diaspora in West Asia contributes significantly to remittances (~$40 billion). If the conflict escalates, remittances may decline, and the safety of Indian emigrants will become a major concern.
Way Forward
- UN Security Council (UNSC) Involvement: The UNSC must step up and broker peace talks between Israel and Lebanon. Global leadership platforms need to be mobilized to prevent the Middle East from becoming a permanent war zone.
- Indirect Negotiations: Third-party mediation (e.g., by the S., EU, or UN) can help lower tensions through indirect negotiations between Israel and Lebanon.
- Strengthening UNIFIL: Enhancing the United Nations Interim Force in Lebanon (UNIFIL) could help maintain peace along the Israel-Lebanon border and prevent further conflicts.
- Demilitarization of Shebaa Farms: The Shebaa Farms area could be placed under international control, reducing the likelihood of future conflicts over the territory.
- Regional Mediation: Countries like Egypt, Jordan, and Saudi Arabia, as well as organizations like the Arab League, could play key roles in mediating peace efforts, stabilizing the region, and supporting conflict resolution.
Conclusion
The Israel-Lebanon war has wide-ranging global and regional impacts, from disrupting geopolitical alignments and global supply chains to affecting India’s economic and strategic interests. Moving forward, it is essential that the international community, through platforms like the UN, and regional actors, work together to mediate peace and prevent further escalation of violence.
MAINS QUESTION
Discuss the historical roots and evolving dynamics of the Israel-Lebanon conflict, with a special focus on the role of Hezbollah and the influence of external actors like Iran. How does this conflict impact the geopolitical stability of the Middle East and what are its implications for global energy security, particularly in the context of India’s economic and strategic interests?

 MPSC राज्य सेवा – 2025
MPSC राज्य सेवा – 2025