Why in News?
Disinformation and hoaxes have evolved from mere annoyance to warfare that can create social discord, increase polarisation, and in some cases, even influence the election outcome. Nation-state actors with geopolitical aspirations, ideological believers, violent extremists, and economically motivated enterprises can manipulate social media narratives with easy and unprecedented reach and scale. The disinformation threat has a new tool in the form of deepfakes.
About Deepfakes
Deepfakes refer to synthetic media created through the application of Artificial Intelligence (AI), where visual and audio content is manipulated or generated. The primary purpose of deepfakes is typically to deceive or mislead individuals. Deepfake gained public attention in 2017 when a Reddit user shared explicit videos featuring celebrities, marking the initial instance. Subsequently, various cases of deepfake occurrences have been documented.
What are Deepfakes?
- Definition: Deepfakes encompass fabricated content, including videos, images, and audio, generated through advanced artificial intelligence (AI) tools.
- Technology: Deepfakes leverage powerful AI algorithms to manipulate and create realistic-looking media with the intent of deceiving or misleading.
- Origin: The term “deepfake” originated in 2017 when a Reddit user, using the username “deepfakes,” shared explicit videos featuring celebrities, bringing attention to this emerging technology.
Technology behind deepfakes
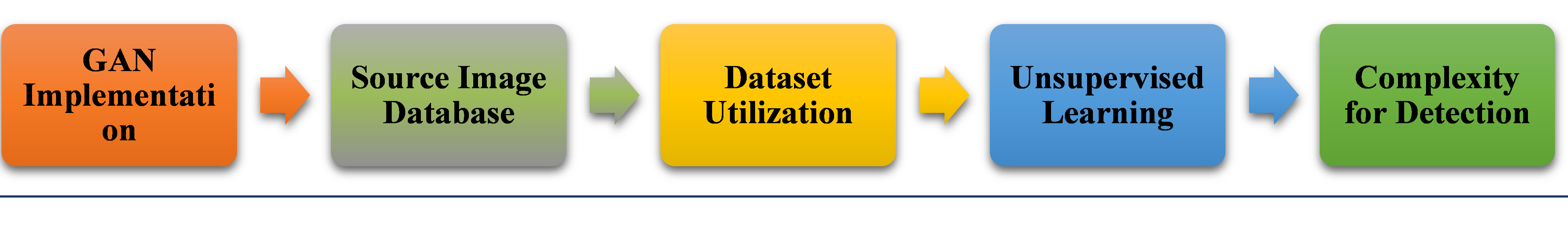
GAN Implementation
- Begin with the application of Generative Adversarial Network (GAN) for image and video manipulation.
- GAN facilitates the detection and replication of subjects’ movements and facial expressions.

Source Image Database
- Utilize a vast database of source images to enhance the realism of deepfake content.
- Select diverse source images, often focusing on public figures, celebrities, and politicians.
Dataset Utilization
- Implement the dataset in one software to generate a fake video.
- Another software is employed to detect signs of forgery in the video.
Unsupervised Learning
- Engage in collaborative work between the two software for unsupervised learning.
- Continue the rendering process until the second software can no longer detect the forgery.
Complexity for Detection
- Result in a process that makes it challenging for other software to identify deepfakes.
- The method involves machine-language models teaching themselves, increasing the difficulty of detection.
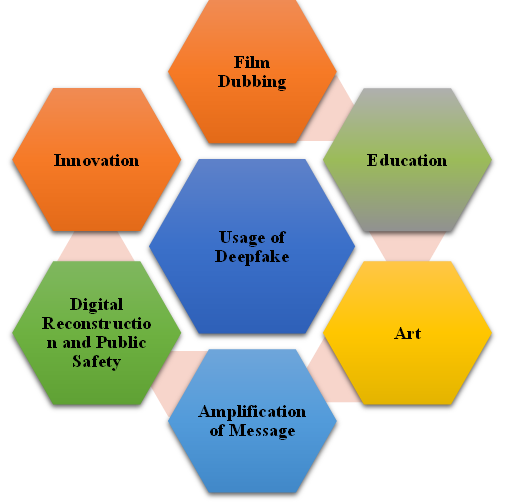
Usage of Deepfake Technology
Film Dubbing: Enables realistic lip-syncing for actors speaking different languages, enhancing film accessibility and immersion for global audiences.
Education: Restores lost voices and recreates historical figures for engaging lessons.
- Example: Deepfake video of Abraham Lincoln delivering the Gettysburg Address for teaching about the American Civil War.
Art: Serves as a creative tool for artists to express themselves or experiment with styles.
- Example: Deepfake video of Salvador Dali interacting with visitors to promote his museum in Florida.
Amplification of Message: Amplifies the impact of individuals with important messages, especially those facing discrimination or censorship.
- Example: Deepfake video of a journalist delivering a final message and calling for justice.
Digital Reconstruction and Public Safety
- Reconstructs missing or damaged digital data, such as restoring old photos or enhancing low-quality footage.
- Creates realistic training materials for emergency responders, law enforcement, and military personnel.
- Example: Deepfake video used to train teachers on responding to a school shooting.
Innovation
- Spurs innovation in entertainment, gaming, marketing, and various industries.
- Enables new forms of storytelling, interaction, diagnosis, and persuasion.
- Example: Deepfake video of Mark Zuckerberg illustrating the potential of synthetic media and its societal implications.
Approaches to tackle Deepfake
Challenges Posed by Deepfakes

Promotion of ‘Liar’s Dividend’
- Liar’s Dividend occurs when undesirable truths are dismissed as deepfake or fake news.
- Leaders exploit deepfakes to replace authentic media, creating confusion between reality and falsehood.
Erosion of Trust in Democratic Processes
- Doctored content, often in the form of realistic fake videos, is presented as fact to manipulate public perception.
- Example: Capitol Hill violence in 2021 incited by the use of deepfake media.
Crime Against Women
- Deepfakes are weaponized to attack the dignity and chastity of women.
- Over 90% of deepfake videos are reported to be pornographic in nature.
Fueling Radicalization and Violence
- Non-state actors, such as ISIS and Al-Qaeda, use fake videos to incite anti-state sentiments.
- Example: Fake videos showing armed forces committing ‘crimes in conflict areas.’
Rise in Cyber Crimes
- Cybercriminals employ deepfake technology for phishing attacks, financial fraud, and identity theft.
- A 230% increase in deepfake usage by cybercriminals and scammers has been observed.
Means of ‘Hybrid Warfare’ or ‘Grey Zone Tactics’
- Countries use deepfakes for spreading misinformation and espionage.
- The European Union terms these deepfakes as ‘Foreign Information Manipulation Interference.’
- Example: China employing deepfakes of injured Indian soldiers by the PLA Army.
Trust Deficit in Traditional Media
- Mainstream news sources can fall for propagandist misinformation, leading to a trust deficit.
- Example: Morphed video of Zelensky asking his soldiers to surrender widely played on mainstream media.

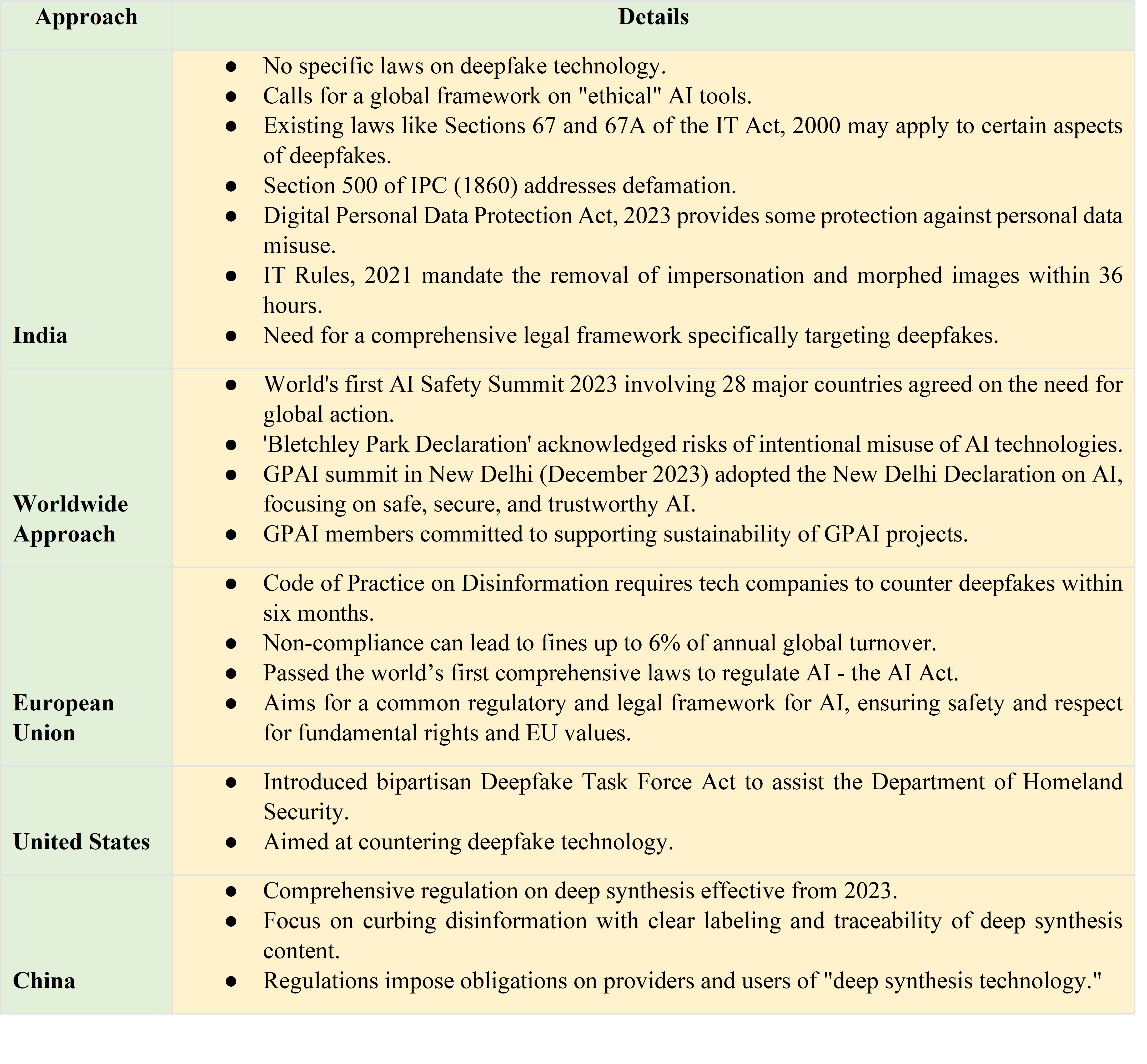
India’s Current Position Regarding Deepfakes

Laws Against Deepfake Technology in India
IT Act of 2000 – Section 66E
Applicable in cases of deepfake crimes involving capturing, publishing, or transmitting a person’s images in mass media, violating their privacy.
Offenders can face imprisonment for up to three years or a fine of up to ₹2 lakh.
IT Act of 2000 – Section 66D
Allows for the prosecution of individuals using communication devices or computer resources with malicious intent to cheat or impersonate someone.
Can result in imprisonment for up to three years and/or a fine of up to ₹1 lakh.
Copyright Protection
The Indian Copyright Act of 1957 provides copyright protection for works, including films, music, and other creative content.
Copyright owners can take legal action against individuals creating deepfakes using copyrighted works without permission.
Section 51 of the Copyright Act stipulates penalties for copyright infringement.
Government Advisory (January 9, 2023)
On January 9, 2023, the Ministry of Information and Broadcasting issued an advisory to media organizations, urging caution when airing content susceptible to manipulation. The ministry recommended labeling manipulated content as “manipulated” or “modified” to inform viewers of alterations.
Implications of Deepfake Technology

- Entertainment Industry: Deepfake technology is applied in the entertainment industry, facilitating the creation of compelling visual effects, digital doubles, and lifelike character animations in movies and video games.
- Social Media and Misinformation: The widespread presence of deepfake content on social media platforms raises concerns about the dissemination of misinformation. Manipulated videos and audio recordings can deceive the public, influencing opinions and perceptions.
- Cybersecurity Threats: Deepfakes present substantial cybersecurity threats as malicious actors can exploit this technology for identity theft, impersonation, and fraud. This endangers the security and privacy of individuals and organizations.
- Political Manipulation and Disinformation: The potential use of deepfake technology in political manipulation and disinformation campaigns raises apprehensions about the integrity of democratic processes and erodes public trust in political institutions.
- Privacy and Consent: Deepfake technology prompts critical inquiries into privacy and consent, particularly regarding the use of individuals’ images and voices without explicit permission.
- Identity Theft and Fraud: The potential for identity theft and fraud through the creation of convincing fake identities using deepfake technology underscores the need for robust legal frameworks to discourage and penalize such malicious activities.
- Impacts on Journalism and Media Integrity: Deepfakes possess the capability to undermine the credibility of journalistic content and media integrity. This challenges the authenticity and trustworthiness of audiovisual evidence.
- Regulatory Challenges: Addressing the ethical and legal implications of deepfake technology requires the development of comprehensive regulatory frameworks. These frameworks must strike a balance between fostering innovation and freedom of expression while safeguarding individuals’ rights and societal integrity.
Way Forward

- Clear Definitions: A specialized legal framework addressing deepfake videos should commence with a precise definition of what constitutes a deepfake, providing clarity for legal interpretation.
- Prohibitions Against Misuse: Incorporate clear prohibitions within the legal framework, outlining specific misuse scenarios for deepfake videos, such as fraud, impersonation, or interference with elections.
- Timely Redressal: Given the rapid dissemination of deepfake videos, the establishment of an agile watchdog mechanism is imperative. This is crucial as traditional legal avenues may operate at a slower pace.
- Involving Social Media Platforms: Impose requirements on social media platforms to actively detect and remove deepfake videos within specified timeframes, ensuring a swift response to curb their spread.
- Legal Remedies: Ensure legal remedies are available for victims of deepfake videos, empowering them to seek recourse against the creators and distributors of such content.
- Protection for Minors: Recognize the potential severe consequences of deepfakes, particularly when involving minors, and implement safeguards to mitigate harm and protect vulnerable individuals.
- Protecting the Rights of the Artist: Strike a balance in the legal framework by safeguarding the rights of artists, emphasizing principles such as fair use, copyright, and the right to privacy. This ensures an equitable approach to the creators of content.

 MPSC राज्य सेवा – 2025
MPSC राज्य सेवा – 2025
