Why In the News?
AI has been recently in the News because of rapid innovations and progress made by pioneers like OpenAI, which is driving a change unprecedented in scale & even with a capacity to create AGI (AI Similar to Humans) by 2028.
Relevance to UPSC
-
Prelims Examination
- Current Events of National and International Importance:
- Developments in AI technology, policies, or significant breakthroughs.
- Government initiatives involving AI.
- General Science:
- Basic understanding of what AI is, how it functions, and its applications in various fields like healthcare, agriculture, transportation, etc.
- Current Events of National and International Importance:
-
Mains Examination
- General Studies-III (Technology, Economic Development, Biodiversity, Environment, Security and Disaster Management):
- Technology: Extensive coverage of AI, its development, applications, and implications for society, economy, and governance.
- Security: Use of AI in cybersecurity, surveillance, and national security.
- Ethical Concerns: Debates on AI ethics, data privacy, and the potential risks associated with AI development.
- Economic Impact: AI’s role in automation, job creation, and job displacement.
- General Studies-III (Technology, Economic Development, Biodiversity, Environment, Security and Disaster Management):
-
Essay Paper
- Candidates might choose to write essays on topics related to AI, exploring its societal impacts, ethical considerations, or its role in shaping future governance.
-
Optional Subjects
- Depending on the candidate’s optional subject, AI might feature directly or indirectly. For instance, in subjects like Public Administration, the use of AI in improving governance and service delivery can be relevant.
What is AI?
AI is a technology that enables machines and computers to simulate human Intelligence and problem-solving capabilities. – Source – IBM
Speaking in simpler terms, AI and its applications with other technologies like Sensors, robotics, etc can enable performing actions that would otherwise require Human Intelligence. Examples – Siri, Alexa, Autonomous cars, ChatGPT, etc.
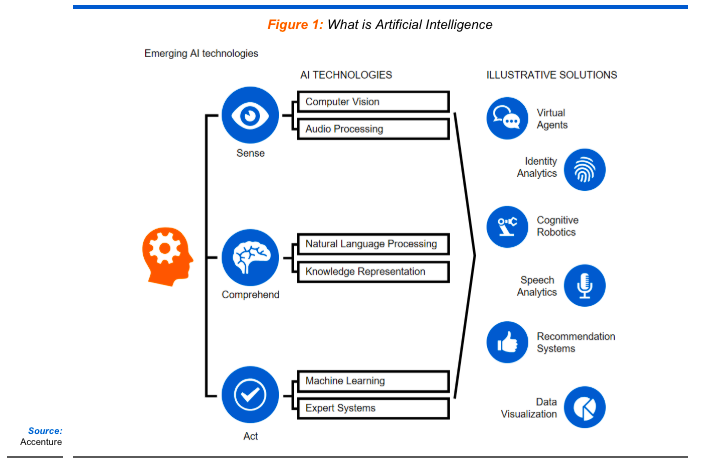
Description – What is AI?
Important terminology in News
Weak AI Vs Strong AI –
- Weak AI, or narrow AI, is designed to handle specific tasks and is prevalent in technologies like Apple’s Siri and self-driving cars. Unlike its name suggests, it powers sophisticated applications despite its specialized scope.
- Strong AI, encompassing artificial general intelligence (AGI) and artificial superintelligence (ASI), remains theoretical. AGI would match human intelligence, while ASI would exceed it. Examples of ASI are mainly found in science fiction, such as the character HAL from the movie “2001: A Space Odyssey.”
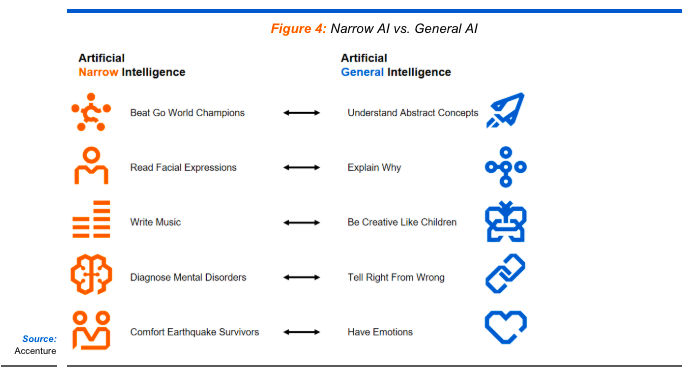
Description – Weak AI Vs Strong AI
What is AGI/ASI –
- AGI, or Artificial General Intelligence, refers to a type of AI that can understand, learn, and apply knowledge across a wide range of tasks, much like a human. It possesses the ability to think abstractly, reason logically, and plan strategically.
- ASI, or Artificial Super Intelligence, goes a step beyond AGI. It represents an AI that surpasses human intelligence and capabilities in all aspects, including creativity, problem-solving, and emotional intelligence. ASI would be more advanced than any human intelligence.
Machine learning vs. deep learning –
- Before understanding ML and DL, it is important to first understand Neural Networks –
- Neural networks are like a mini-brain for computers, helping them learn and make decisions. They have layers of “neurons” — little units that work together to process information. You start with the input layer, where you give the network some data. Then, the data goes through several hidden layers where the learning happens, and finally, the output layer gives you the result or answer. The more examples the network sees, the better it gets at recognizing patterns, just like how studying more helps you do better on tests. This technology is what lets your phone recognize your voice or suggests videos you might like.
- Machine learning and deep learning are both branches of AI that utilize neural networks, structures inspired by the human brain, to process and learn from data. Machine learning generally involves simpler neural networks with a few layers and relies on structured, labeled data. It often needs human input to guide the learning process.
- Deep learning, a subset of machine learning, uses more complex neural networks with many layers, allowing it to learn from vast amounts of both structured and unstructured data without much human intervention. This enables it to recognize patterns and make predictions more autonomously.
- For example, a machine learning algorithm might require labeled photos to learn to recognize cats, whereas a deep learning algorithm could learn to identify cats from a mixed set of unlabeled images by itself.
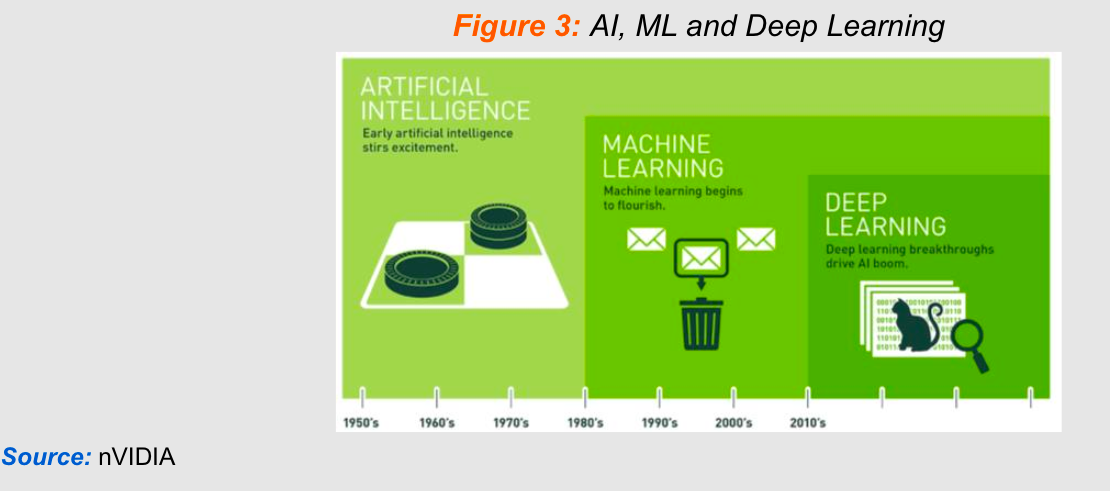
Description – Evolution of AI, Source – NVidia
Classification of AI based on functionality –
- Reactive Machine AI focuses solely on current data for specific tasks, e.g., IBM Deep Blue.
- Limited Memory AI, like ChatGPT and Siri, uses recent data without long-term memory.
- Theory of Mind AI, still theoretical, aims to understand emotions, as seen in Emotion AI.
- Self-aware AI would possess self-awareness and emotions.
What is ChatGPT and How does it work?
- What is ChatGPT?
- ChatGPT is like a virtual assistant that can write and chat with you as if it were a human. Developed by OpenAI, it’s designed to follow a conversation or a piece of writing and continue it in a way that seems natural. Imagine you wrote down half a sentence, and ChatGPT cleverly completes it for you!
- How Does ChatGPT Work?
- ChatGPT works by predicting what word comes next in a sentence. It has read a vast amount of text from the internet, books, and more, so it has learned how sentences typically flow. When you give it a starting point, like a few words or a question, it uses what it’s understood to guess the next word, then the next, and so on.
- The Magic Behind ChatGPT
- Training with Examples: Think of ChatGPT as having gone through massive books of examples. It has seen countless ways people write and talk. When you start a sentence, it thinks, “What have I seen before that looks like this?” and tries to complete it similarly.
- Ranking Choices: ChatGPT picks more than just the most obvious next word. It often chooses a less common option to make the conversation more interesting. It’s like sometimes choosing a less traveled path on a hike to see where it leads.
- Using Probabilities: Each word it picks comes with a probability, a measure of how likely that word is to follow the previous one. Sometimes, to avoid boring or repetitive text, it picks a less likely word.
- Temperature Setting: ChatGPT has a setting called “temperature” that affects its choices. A higher temperature means it’s more likely to pick unusual words, making the text more varied and creative.
- Why Does ChatGPT Work Well?
- Despite its simplicity in choosing words based on probability, ChatGPT can generate impressively human-like text. This tells us something important about language: it’s more structured and predictable than we might think. ChatGPT’s ability to create meaningful sentences suggests that language follows certain patterns that the model has learned to predict.
- What was the innovation by the Open AI team that changed the landscape of AI?
- ChatGPT represents a significant advancement in AI through its use of the Transformer architecture, which fundamentally changes how the machine understands and generates text. Unlike older models that process words one by one and often miss the broader context, ChatGPT can look at entire sentences or paragraphs at once, recognizing how words relate to each other across longer stretches of text. This ability helps it grasp the overall meaning and produce responses that are not only relevant but also contextually aware.
Impact and implications for the future –
Impact on Countries: A Spectrum from Developed to Emerging
- Developed nations like Singapore, the USA, and Denmark are leading AI integration, enhancing productivity but risking job displacement and wage inequality with 60% of jobs impacted. Emerging markets face a 40% job impact, with potential growth through improved digital infrastructure and education to mitigate AI-driven inequalities. Low-income countries, with a 26% impact rate, risk being left behind without global collaboration to leverage AI benefits. This transformation across different economic strata highlights both opportunities and challenges in the AI landscape
Impact on the Economy, society, and polity –

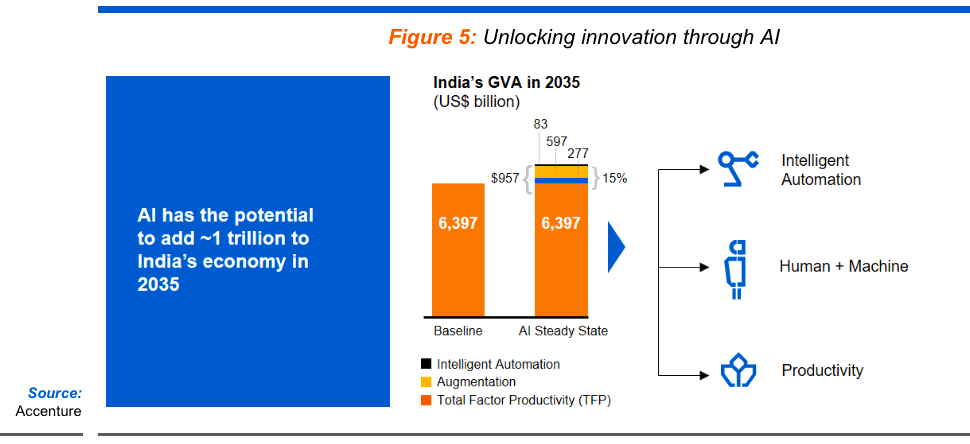
Economy
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) is transforming global economies and presents a unique opportunity for India. Globally, in the U.S., industry leaders like Microsoft and Google are catalyzing economic growth by driving AI innovations with substantial private investments. Similarly, China is aggressively funding AI, with plans to establish a $150 billion AI industry by 2030, showcasing how strategic state support can accelerate technological development. In Europe, the EU’s investment of €700 million in AI research emphasizes the role of public-private partnerships in enhancing competitiveness.
- For India, AI offers significant economic and social development prospects. According to Accenture, AI could boost India’s annual growth rate by 1.3 percentage points by 2035. The potential includes increasing healthcare access, enhancing agricultural productivity, and improving education and infrastructure through intelligent solutions tailored to India’s unique challenges. This integration across sectors positions India to not only advance its economy but also serve as a crucial AI hub for other developing nations, embodying the role of an “AI Garage” for 40% of the world.
Service Sectors: Enhanced Customer Experiences and Efficiency
- In the service sector, AI’s impact is just as significant. The use of chatbots and virtual assistants is expected to augment human roles rather than replace them, with a Gartner report estimating that by 2021, AI augmentation will generate $2.9 trillion in business value. Jobs in customer service have transformed, with AI handling up to 80% of all customer interactions, according to a Salesforce study. This shift requires customer service professionals to manage more complex inquiries and oversee AI operations, reshaping the nature of service jobs towards higher-level customer engagement and technical oversight.
Sovereignty and Global Dynamics: Navigating the AI Landscape
- As AI becomes a staple in national development strategies, its impact on sovereignty and the global power structure is becoming more evident. For instance, the United States and China are leading the AI arms race, with China announcing its goal to become a $150 billion AI global leader by 2030. This ambition is reflected in the 20-fold increase in AI-related patent submissions in China from 2005 to 2017. The economic clout and technological independence brought by AI advancements are poised to redefine traditional geopolitical alliances and potentially shift the balance of power internationally.
Warfare: The Autonomous Arms Race
- In the domain of warfare, the adoption of AI is accelerating at a rapid pace. Global military spending on AI is projected to grow from $6.26 billion in 2017 to $18.82 billion in 2025, according to a report from Markets and Markets. Autonomous drones and robotics, equipped with AI, have seen a 600% increase in military applications over the last decade. These developments raise urgent questions about the future of combat and the potential for AI-driven conflicts, with experts from the Stockholm International Peace Research Institute warning that the lack of international regulatory frameworks for autonomous weapons could lead to new types of uncontrolled warfare. This scenario underscores the need for clear protocols and international agreements to govern the militaristic use of AI and ensure global stability.
Challenges –
- AI’s ethical and social implications in India are profound, given its rapid digital transformation and diverse demographics. AI systems may exhibit biases, as demonstrated in a 2019 MIT Media Lab study showing facial recognition’s lower accuracy with darker-skinned women. To mitigate bias, India must diversify its AI training datasets, which are currently limited to a few research centers.
- Privacy issues are heightened by expansive digital identity programs like Aadhaar, lacking robust protections akin to Europe’s GDPR. Stronger regulations on AI and privacy are essential to safeguard individual rights and ensure equitable AI benefits.
- The employment landscape is also shifting dramatically due to AI. The World Economic Forum predicts AI and automation will globally displace 75 million jobs but create 133 million new ones by 2022. In India, this transition demands significant educational reforms and skilling initiatives to prepare the workforce for AI-driven roles, particularly as high-skill jobs may exacerbate income inequalities without inclusive strategies.
- Security risks in AI are notable, with adversarial attacks posing threats to systems like autonomous vehicles—a study by Cornell University highlighted such vulnerabilities. The potential for AI’s militarization, such as autonomous drones and decision-making systems, calls for stringent international regulations to prevent an arms race, underscored by the Stockholm International Peace Research Institute.
- Governance and regulation need urgent attention as AI becomes integral to critical sectors like healthcare and defense. India lacks a comprehensive AI regulatory framework, risking misuse. The AI Now Institute stresses the importance of strong governance structures to oversee AI development responsibly. Moreover, existing intellectual property laws must evolve to address the unique challenges AI-generated content poses.
- AI’s “black box” decision-making processes, particularly in deep learning models, obstruct transparency and accountability. Research into making AI decisions more understandable is crucial, especially for critical applications in healthcare and criminal justice.
- Data challenges are significant, with the need for high-quality, unbiased data paramount to effective AI deployment. Public perception and societal resistance also need addressing through education and dialogue to build trust and understanding of AI’s benefits and risks.
- Culturally, the integration of AI in social interactions must respect and preserve India’s strong community bonds, ensuring technology enhances rather than undermines human connectivity.
Way ahead –
- Enhancing Ethical Frameworks: Develop universal ethical guidelines for AI, inspired by the GDPR, through collaborations between bodies like the United Nations and the International Telecommunication Union. These should cover fairness, transparency, and accountability. Additionally, implement AI impact assessments before deploying new systems, especially in sensitive areas like policing and healthcare. Ex: Montreal Declaration calls for responsible development of AI.
- Fostering Economic Equity: Support workforce transitions through lifelong learning and re-skilling programs. Expand social safety nets, including universal basic income trials, to help those displaced by AI.
- Strengthening Security Measures: Invest in research to create AI systems resistant to adversarial attacks and regulate autonomous weapons with international treaties to ensure global security.
- Promoting Transparent Governance: Increase transparency in AI systems’ operations and establish independent monitoring bodies like the Financial Stability Board to oversee AI’s impacts and prevent misuse.
- Investing in AI Literacy and Public Engagement: Enhance AI education at all levels and facilitate public dialogues on AI’s societal impacts through platforms like citizen assemblies.
- Advancing International Collaboration: Encourage global partnerships and coordinate international efforts to standardize AI interoperability, security, and efficiency, as seen with initiatives like the Global Partnership on Artificial Intelligence (GPAI).
Strategic Roadmap for AI Adoption in India
- India’s strategy to become an AI leader involves enhancing research, data management, education, regulatory frameworks, and international collaboration:
- Research and Development: Boost funding, establish AI excellence centers, and promote market-oriented research through public-private partnerships.
- Data and Integration: Develop high-quality annotated datasets and reduce infrastructural costs to facilitate AI adoption.
- Education and Workforce: Update curricula and offer vocational training in AI technologies.
- Regulation and Ethics: Implement strict privacy laws and ethical AI guidelines.
- Intellectual Property and Governance: Reform IP laws and strengthen governance to support AI innovation and ensure responsible development.
- Global Collaboration: Enhance international partnerships for shared AI advancements.
India can learn significant insights from other countries’ AI development strategies:
United States:
- Private Sector Leadership: Leverage the strengths of the private sector to drive AI innovation and growth, as seen with major companies like Microsoft, Google, and IBM leading the way in AI research and application.
- Cluster Development: Emphasize the creation of AI hubs like Silicon Valley, which bring together talent, universities, and private investment to foster innovation and technological advancements.
China:
- Government Funding and Planning: Implement structured government investment in AI, such as the ambitious plan to establish a $150 billion AI industry by 2030, with significant funding for universities and public sector projects.
- Clear Milestones and Governance: Develop a clear, long-term development plan with specific milestones and governance structures to guide AI development, boosting confidence among potential investors and stakeholders.
United Kingdom:
- Academic-Industry Collaboration: Strengthen ties between academia and industry to convert research into commercial success, as evidenced by collaborations that led to the creation of AI startups like DeepMind, VocalIQ, and SwiftKey.
- Focused Research Funding: Provide substantial funding for AI research through grants and trusts to sustain innovation, similar to the GBP 80 million annually from the Leverhulme Trust and support from The Alan Turing Institute.
European Union:
- Public-Private Partnerships: Enhance AI development through robust public-private partnerships, with significant investment in foundational and applied AI research, as seen with the EU’s Robotics Public Private Partnership allocating EUR 700 million to research.

 MPSC राज्य सेवा – 2025
MPSC राज्य सेवा – 2025
