Introduction
- Context of AI in Healthcare: India’s healthcare system faces significant challenges, including inadequate infrastructure, shortage of healthcare professionals, and uneven access to quality care across its diverse population. In recent years, there has been a growing interest in utilizing Artificial Intelligence (AI) to address these persistent gaps.
- Promise of AI: AI technologies offer the potential to increase efficiency, improve access to medical expertise, and revolutionize healthcare delivery in a country where resources are often stretched thin.
- Critical Concerns: However, integrating AI in healthcare, especially in a complex country like India, raises questions about feasibility, sustainability, and ethical implications. AI’s lack of human qualities such as empathy, cultural understanding, and the ability to handle nuanced patient conditions necessitates a balanced approach.
- Need for Strategic Approach: As India explores AI’s potential, it must weigh the benefits against addressing foundational healthcare issues and developing comprehensive regulations to ensure AI tools adhere to the core medical ethic of “Do No Harm.”
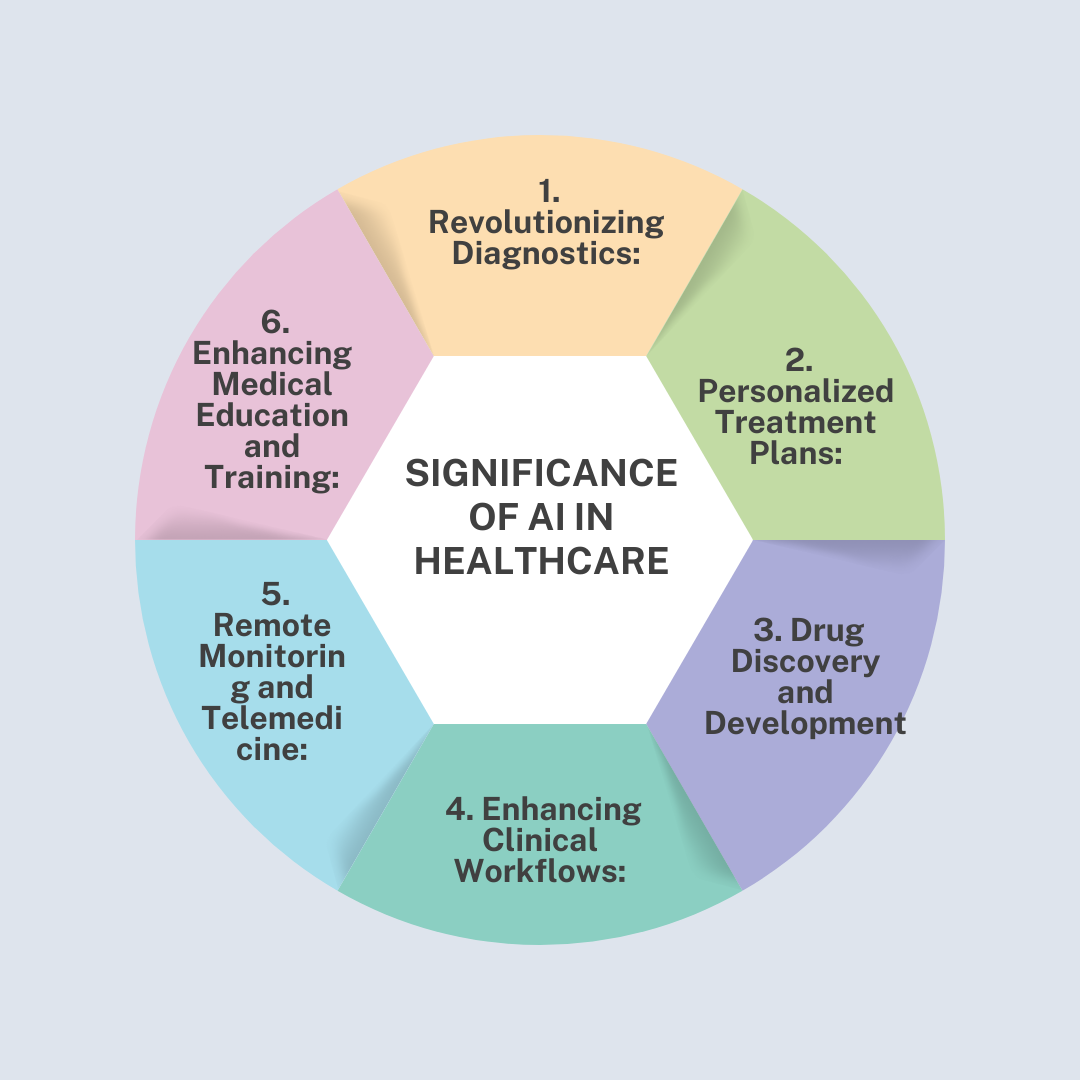
Significance of AI in Healthcare
- Revolutionizing Diagnostics:
- Enhanced Accuracy and Speed: AI is transforming medical diagnostics with unprecedented accuracy and speed.
- Detection Capabilities: AI algorithms, especially in radiology, detect subtle abnormalities that might be missed by human eyes.
- Case Example: A 2020 study in Nature demonstrated that AI reduced false-positive and false-negative rates in breast cancer detection by 1.2% and 2.7%, respectively.
- Broader Impact: AI holds the potential to improve diagnostic accuracy across fields like ophthalmology and pathology.
- Personalized Treatment Plans:
- Precision Medicine: AI enables precision medicine by analyzing vast amounts of patient data to create personalized treatment plans.
- Targeted Therapies: AI considers genetic makeup, lifestyle factors, and medical history, recommending therapies with higher efficacy and fewer side effects.
- Example: IBM Watson Oncology has assisted oncologists in over 230 hospitals worldwide to develop personalized cancer treatments, improving patient outcomes and optimizing resources.
- Drug Discovery and Development:
- Accelerated Processes: AI is dramatically accelerating drug discovery and development, bringing life-saving medications to market faster and at lower costs.
- Machine Learning Use: AI algorithms analyze biological data, predict drug-target interactions, and optimize molecular structures, significantly reducing the time and resources needed.
- Success Story: Insilico Medicine used AI in 2020 to design, synthesize, and validate a novel drug candidate for fibrosis in just 46 days, a process that traditionally takes years.
- Enhancing Clinical Workflows:
- Streamlining Operations: AI reduces administrative burdens and allows healthcare professionals to focus on patient care.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): NLP algorithms transcribe and summarize doctor-patient conversations, update electronic health records (EHRs), and generate clinical notes.
- Improving Efficiency: AI-driven scheduling systems optimize patient flow, reduce wait times, and enhance resource allocation in hospitals.
- Remote Monitoring and Telemedicine:
- Expanding Access: AI-powered wearables and IoT devices monitor patient vitals remotely, improving access to healthcare.
- AI in Telemedicine: During the COVID-19 pandemic, AI-based telemedicine platforms like Babylon Health used AI chatbots for patient triage and consultations.
- Rural Impact: This is particularly beneficial for rural and underserved areas where access to specialists is limited.
- WHO’s Sarah Prototype: An AI-driven digital health promoter available 24/7 in multiple languages, providing health tips and information.
- Enhancing Medical Education and Training:
- Personalized Learning: AI-powered platforms provide tailored learning experiences and simulate complex clinical scenarios.
- Virtual and Augmented Reality (VR/AR): AI-driven VR/AR platforms create immersive training environments for medical professionals.
- Example: FundamentalVR uses AI-driven haptic VR systems, allowing surgeons to practice procedures with realistic feedback.
Major Challenges of AI in Healthcare in India
- Infrastructure Limitations:
- Technological Gaps: Many healthcare facilities, especially in rural and semi-urban areas, lack the necessary infrastructure to support AI.
- Electricity and Connectivity Issues: Only 45% of Health and Wellness Centres in rural India have electricity backup, complicating AI deployment.
- Data Challenges:
- Fragmented Healthcare System: A diverse system with public and private providers results in inconsistent data collection practices.
- Lack of Integration: Absence of standardized data integration and retention guidelines impedes effective AI model training.
- Digital Divide:
- Unequal Access: Urban areas are more likely to benefit from AI-driven healthcare solutions, while rural regions lack digital infrastructure.
- Internet Accessibility: As of 2023, 45% of the Indian population lacks internet access, limiting the reach of AI technologies.
- Regulatory Hurdles:
- Lack of Comprehensive Regulations: No specific regulations for AI in healthcare create uncertainty and slow innovation.
- Pending Legislation: The Digital Information Security in Healthcare Act (DISHA) proposed in 2017 remains unenacted, leaving a regulatory vacuum.
- Ethical and Cultural Considerations:
- Algorithmic Bias: AI models trained on Western datasets may not be fully applicable to India’s diverse population.
- Cultural Sensitivities: Varying health literacy levels and cultural norms add complexity to AI implementation.
- Cost and Resource Allocation:
- High Initial Costs: Implementing AI in healthcare involves substantial initial investments, ranging from USD 20,000 to USD 1,000,000.
- Limited Healthcare Spending: India’s healthcare expenditure is relatively low, making such investments challenging.
- Language and Localization Issues:
- Linguistic Diversity: India’s 22 official languages and numerous dialects complicate AI development for effective communication.
- Risk of Miscommunication: Language barriers may lead to misdiagnosis and reduced effectiveness of AI tools.
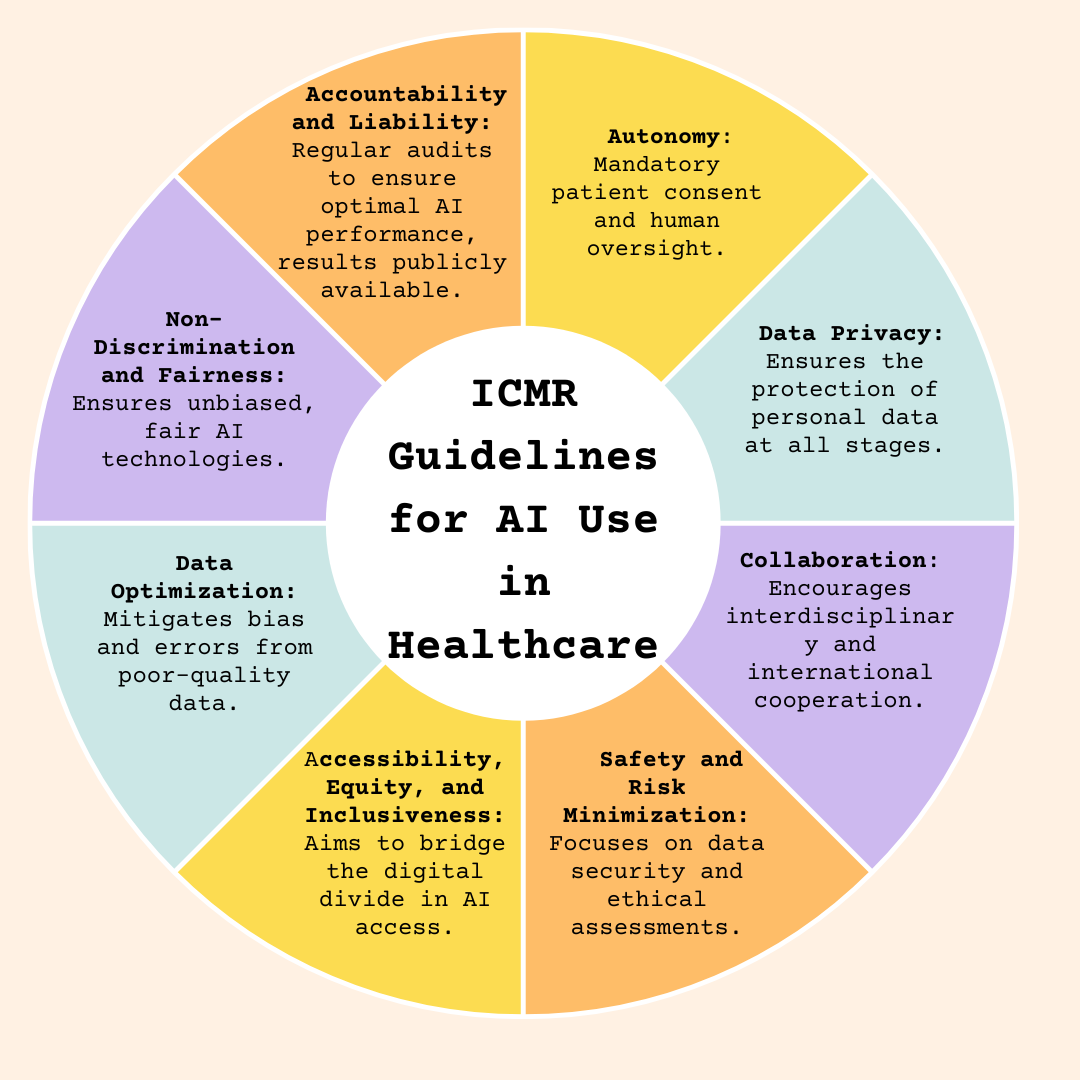
ICMR Guidelines for AI Use in Healthcare
Ethical Principles by ICMR (March 2023): Ten patient-centric ethical guidelines for AI use in healthcare:
Supporting Frameworks: Include the Digital Health Authority under the National Health Policy (2017), DISHA 2018, and Medical Device Rules, 2017.
Strategies for Effective AI Implementation in Healthcare in India
- Strengthen the National Health Resources Database:
- Integrate AI with NHRR: Enhance the National Health Resources Repository (NHRR) with AI-ready data protocols.
- Model After Estonia’s e-Health: Use Estonia’s e-Health system, which covers 95% of the population’s health data, as a benchmark.
- Develop India-specific AI Models:
- Tailored Solutions: Collaborate with academia and tech companies to create AI models suitable for India’s diverse healthcare needs.
- Localized Datasets: Train AI on datasets reflecting India’s genetic diversity, regional disease patterns, and socio-economic factors.
- Create a Tiered AI Implementation Strategy:
- Urban vs. Rural Focus: Implement advanced AI in urban tertiary hospitals and simpler AI tools in rural areas.
- Expand Initiatives: Build on programs like ‘NITI Aayog AI for All’ and the Aarogya Setu app.
- Establish a Regulatory Sandbox for Healthcare AI:
- Controlled Testing Environment: Develop a ‘Regulatory Sandbox’ to test AI solutions under regulatory supervision, modeled after RBI’s fintech sandbox.
- Integrate AI Education in Medical Curriculum:
- Curriculum Enhancement: Include AI and data science modules in medical and nursing education.
- Partnerships for Training: Partner with online platforms for certified AI courses and internships.
- Establish Ethical Guidelines for AI in Healthcare:
- Create an AI Ethics Committee: Form an AI Ethics Committee under the Ministry of Health to address data privacy, bias, and clinical decision-making.
- Create AI-Ready Healthcare Infrastructure:
- Upgrade Digital Infrastructure: Ensure stable electricity, robust internet, and necessary hardware in healthcare centers.
- Utilize Existing Schemes: Leverage the National Rural Health Mission for digital infrastructure upgrades.
- Launch Public Awareness Campaigns:
- Educate the Public: Conduct campaigns to explain AI’s benefits and limitations using various media and community outreach

 UPSC GS Foundation Prelims+Mains for 2026
UPSC GS Foundation Prelims+Mains for 2026